This report is one of a series on the adjustments we make to convert GAAP data to economic earnings.
Reported earnings don’t tell the whole story of a company’s profits. They are based on accounting rules designed for debt investors, not equity investors, and are manipulated by companies to manage earnings. Only economic earnings provide a complete and unadulterated measure of profitability.
Converting GAAP data into economic earnings should be part of every investor’s diligence process. Performing detailed analysis of footnotes and the MD&A is part of fulfilling fiduciary responsibilities.
We’ve performed unrivaled due diligence on 5,500 10-Ks every year for the past decade.
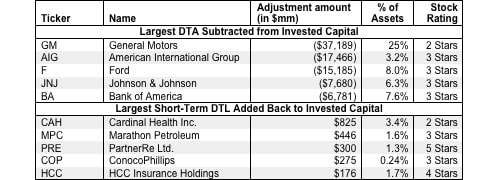
Deferred tax assets (DTAs) arise when reported income on a financial statement is less than taxable income. DTAs are, in a sense, like pre-paid taxes and represent expected reductions of future reported taxes. Deferred tax liabilities (DTLs), on the other hand, arise when reported income is greater than taxable income. DTLs represent the expected amount of additional reported taxes to be paid. These items are a result of differences between GAAP accrual accounting and tax policy. Examples of DTAs include: product warranty reserves, tax loss carry-forwards, and future pension and post-retirement benefit payments. Examples of DTLs include: accelerated depreciation payments and nondeductible intangibles.
DTAs artificially raise reported assets and do not help generate operating profit while DTLs are like a source of interest-free financing. We remove the impact of DTAs and DTLs from our calculation of invested capital to ensure the more accurate measure of a firm’s return on invested capital (ROIC).
We subtract all DTAs from invested capital. We include all DTLs in invested capital. When we calculate a firm’s implied value in our DCF model, we subtract any net DTLs (DTLs minus DTAs) as they are real cash obligations on future cash flows.
DTAs and DTLs are disclosed in two ways. They are either explicitly presented as DTAs and DTLs or hidden in other line items on the balance sheet, in which case investors have to dig through the footnotes to find them.
10 replies to "Deferred Tax Assets and Liabilities – Invested Capital Adjustment"
Hi,
I understand how the numerator in ROIC is Operating Income * (1-t), however why would Invested Capital be constrained to Operating Asset – Operating Liabilities? If you defined it as money put in place by creditors and shareholders, then deferred tax liabilities (free financing from the government) help ease the required financing from creditors and shareholders. Any amount of DTL is money that is not needed from creditors and shareholders, and should therefore reduce the IC, so I don’t understand why you add it back.
Thanks
Deferred Tax Liabilities are essentially a form of interest free debt. In fact, Warren Buffett has talked about DTL’s are an important form of low-cost financing for Berkshire. He wrote in 1996: “Berkshire has access to two low-cost, non-perilous sources of leverage that allow us to safely own more assets than our equity capital alone would permit: deferred taxes and “float”… In effect, they give us the benefit of debt – an ability to have more assets working for us – but saddle us with none of its drawbacks.”
Yes, so why remove DTLs?
We don’t remove DTLs from invested capital. The adjustment we make is to add back short-term DTLs (which would normally be counted as non-interest bearing current liabilities and deducted from invested capital). Apologies if the article is not clear on that point.
Do you add back the change in deferred taxes to Net Income to get NOPAT?
Yes, that is one of the many adjustments we make. For more details on how we calculate Cash Operating Taxes: https://www.newconstructs.com/non-operating-tax-adjustment/.
More details on NOPAT here: https://www.newconstructs.com/education-net-operating-profit/
Hi David, when you say, “.. When we calculate a firm’s implied value in our DCF model, we subtract any net DTLs (DTLs minus DTAs) as they are real cash obligations on future cash flows.. ” , do you mean that to calculate equity value we subtract DTLs (DTLs minus DTAs) from enterprise value (i.e. firm value)? Awaiting you kind reply.
Siddharth, thank you for your question. The value of an asset is the present value of future cash flows. Since net DTLs are obligations on future cash flows, we subtract net DTLs from our calculation of the present value of future cash flows in our DCF model.
Thanks Matt. So we will subtract net DTL from Enterprise Value to arrive at Equity Value; right ?
Siddharth,
Thanks for your question. Enterprise value and shareholder value from our discounted cash flow model are two distinct concepts. Enterprise value represents the market value of the firm to all stakeholders. You can see how we treat net DTLs in our calculation of Enterprise Value here.
We use our reverse DCF model to quantify the expectations implied by a firm’s current shareholder value. In doing so, our model calculates the present value of the firm’s future cash flows and adjusts for senior claims to equity holders or assets that are accretive to equity holders to calculate shareholder value. You can see how we treat net DTLs in our discounted cash flow model here.