We published an update on this Danger Zone pick on January 31, 2022. A copy of the associated Earnings Update report is here.
Rivian (RIVN: $52 billion expected valuation), an electric truck and delivery van manufacturer, is set to IPO next week with an expected valuation of ~$52 billion, the midpoint of its IPO price range. A $52 billion valuation is well below the $80 billion valuation the company originally sought, but it is still too high.
Despite the popularity of the electric vehicle market and huge gains in Tesla’s stock (TSLA), we think investors should avoid the temptation to buy Rivian shares.
We are skeptical that Rivian’s IPO will deliver for investors, even with the lower valuation. Investors shouldn’t buy a stock just because it’s in a hot sector.
Rivian has yet to manufacture a meaningful number of vehicles and competes with well-capitalized electric vehicle upstarts as well as incumbents like General Motors (GM) and BMW, which both have decades of experience and multi-billion dollar plans to expand EV production.
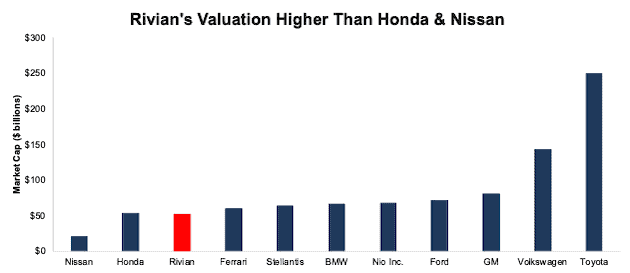
Rivian’s $52 billion valuation is about the same as Honda (HMC), which has world-class manufacturing capabilities and is investing heavily in a suite of electric vehicles. It makes no sense for Rivian to IPO with a valuation anywhere near Honda. Maybe, after several years of production and sales on par with Honda, Rivian would deserve a comparable valuation. But, to buy the stock at such a high price before the company has shown it can consistently produce more than a handful of cars seems ridiculous to us.
Rivian’s $52 billion valuation implies that Rivian will sell 2 million vehicles in 2030, or nearly 2.5 times the number of Tesla (TSLA) vehicles produced over the past 12 months and 66% more vehicles than Honda sold in the U.S. in 2020.
These manufacturing milestones are highly improbable given Rivian’s lack of manufacturing infrastructure and experience as well as the intense competition it faces in the EV market.
Investments from Amazon and Ford do nothing to justify the IPO valuation. Those investments were made at much lower prices and simply position these companies to participate in what appears to be a very lucrative IPO for private investors and owners.
We believe the stock is worth $13 billion at best – a 75% downside to the midpoint IPO valuation of $52 billion.
Below, we’ll outline the impracticality of Rivian meeting the expectations baked into the expected IPO valuation.
$52 Billion Valuation Makes No Sense
At its expected valuation of ~$52 billion, Rivian would be valued on par with Honda, a manufacturer that produced over 4.5 million vehicles worldwide in fiscal 2021, and nearing Stellantis, BMW, and more. See Figure 1. At $1.2 trillion, Tesla’s (TSLA) market cap is off the chart and is therefore excluded from Figure 1.
Figure 1: Rivian’s Expected Valuation Compared to Competition
Sources: New Constructs, LLC and company filings
At Least Tesla Sold Vehicles Prior to IPO
With no revenue from actual vehicle sales, investors need to understand that Rivian is in its infancy. Unsurprisingly, Core Earnings[1] were -$398 million in 2019 and -$982 million in 2020 and the company burned -$2.5 billion in free cash flow (FCF) in 2020. In other words, the company looks more like a startup than one ready for an IPO. When Tesla went public in 2010 at a valuation of ~$1.7 billion, it was already delivering vehicles, and by the end of 2010, delivered over 1,500 units.
Valuation Implies Rivian Will Take Huge Share of the Global EV Market
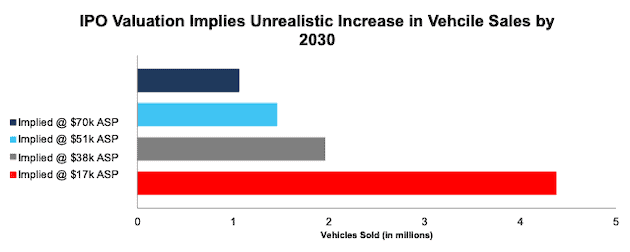
With less than 200 deliveries of its R1T vehicle, Rivian doesn’t have significant sales to generate a meaningful average selling price (ASP) for its vehicles. However, if we optimistically assume the starting price of $70,000 for its R1S as its ASP, Rivian’s expected valuation implies the company will sell 1.1 million vehicles in 2030, or 4% of the projected global EV passenger vehicle market in 2030.
Meanwhile, Bloomberg reports that Rivian is gearing up for production of upwards of 300,000 units, or just one-fourth the production implied by its expected IPO valuation. We think it is unlikely that Rivian will sell such a high volume of vehicles at a $70,000 ASP, and the implied vehicle sales based on lower ASPs look even more impractical.
Per Figure 2, Rivian’s midpoint IPO valuation implies that, in 2030, it will sell the following number of vehicles based on different ASPs:
- 1.1 million vehicles – ASP of $70k (starting price of Rivian’s R1S)
- 1.5 million vehicles – ASP of $51k (equal to Tesla over TTM)
- 2.0 million vehicles – ASP of $38k (average new car price in the U.S. in 2020)
- 4.4 million vehicles – ASP of $17k (equal to General Motors over the TTM)
If Rivian achieves those EV sales, the implied market share for the company would be the following (assuming global passenger EV sales reach 25.8 million in 2030, the base case projection from the IEA):
- 4% for 1.1 million vehicles
- 6% for 1.5 million vehicles
- 8% for 2.0 million vehicles
- 17% for 4.4 million vehicles
Figure 2: Implied Vehicle Sales in 2030 to Justify Expected Valuation
Sources: New Constructs, LLC and company filings
Buying stock in any company at a price that implies such huge market share gain is ill-advised, in our opinion.
Doing the Math: $52 Billion Valuation Is Beyond Overvalued
We use our reverse discounted cash flow (DCF) model to provide more clear, mathematical evidence that the expected IPO valuation is too high and offers unattractive risk/reward.
In order to justify the midpoint of its IPO price range, Rivian must:
- Immediately achieve a 6% NOPAT margin (slightly below Tesla’s TTM margin) and
- grow revenue to $74 billion by 2030 (over 1.5x Tesla’s TTM revenue).
In this scenario, Rivian would generate $74 billion in revenue in fiscal 2030, which is 57% and 55% of General Motors’ (GM) and Ford’s (F) TTM revenue. This implied revenue is also used to calculate the implied vehicle sales in Figure 2 above, which are so high they warrant repeating. At an ASP of $70k, this scenario implies Rivian sells ~1.1 million vehicles in 2030, or 4% of the forecasted global EV passenger vehicle market in 2030. For reference, Honda sold 1.2 million vehicles in the U.S. in 2020.
DCF Scenario 2: Growth at 5x Industry Expectations Equals 75% Downside
We review an additional DCF scenario to highlight the downside risk even if Rivian’s revenue grows five times the expected industry growth rate.
If we assume Rivian:
- immediately achieves a NOPAT margin of 6% and
- grows revenue to $25 billion by 2030, then
RIVN is worth just $13 billion today – a 75% downside to the midpoint IPO valuation. See the math behind this reverse DCF scenario. In this scenario, Rivian would generate $24.7 billion in revenue in 2030, which is equal to Tesla’s 2019 revenue. At an ASP of $38k, the average new car price in the U.S. in 2020, this scenario implies Rivian sells 650 thousand vehicles in 2030, which is 110% of the number of Chevrolet Silverado’s sold in 2020 and 83% of the F-150s sold in 2020. For reference, this level of production is also 4x the maximum production capacity of the company’s Normal Factory.
Based on our reverse DCF model, if the company cannot achieve at least five times the expected industry growth rate, the downside could be as much as 100%.
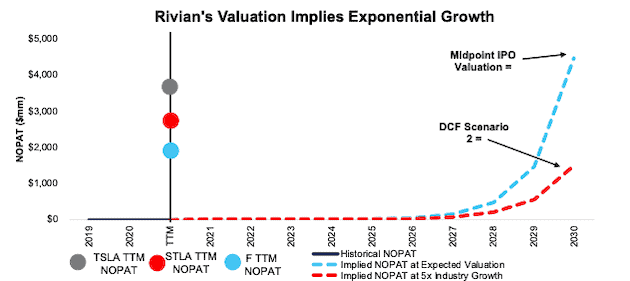
Figure 3 compares Rivian’s historical NOPAT to the NOPAT implied by each of the above DCF scenarios. For additional context, we show Tesla’s, Stellantis’, and Ford’s TTM NOPAT. Notably, Honda’s TTM NOPAT, at $6.2 billion, is literally off the chart and is, therefore, excluded from Figure 3.
Figure 3: Rivian’s IPO Valuation is Unreasonably High
Sources: New Constructs, LLC and company filings
Both of the above scenarios also assume Rivian grows revenue, NOPAT, and FCF without increasing working capital or fixed assets. This assumption is highly unlikely, especially given Rivian will need additional manufacturing plants to reach the production levels implied by its valuation, but allows us to create best-case scenarios that demonstrate the level of expectations embedded in the current valuation.
Roadblocks to Justifying Rivian’s High Valuation
Below, we present a few of the many challenges Rivian faces as it attempts to meet the expectations implied by its expected IPO valuation.
Incumbents Are Coming for the EV Crown
Incumbent automakers are highly profitable and generate billions in free cash flow by leveraging scale and manufacturing expertise. The advantages that incumbents have accumulated in the traditional auto market make their transition to the EV market easier than new entrants like Rivian and Tesla.
We know from Tesla’s early days (filled with setbacks and delays) that it takes years to develop scale and manufacturing capabilities to routinely deliver a large number of quality vehicles on time. Rivian, despite investments from Ford that could help alleviate some early growing pains, has already delayed delivery of its flagship vehicles. Any further delays could make some of the company’s pre-ordering customers, which total ~54,000 as of October 31 for its passenger vehicles, look elsewhere. For comparison, Ford announced in October 2021 that it had over 160,000 reservations for its F-150 Lightning.
In actual manufacturing, and not pre-orders, Ford, Volkswagen, General Motors, and on a smaller level Tesla, have already developed the necessary infrastructure to deliver vehicles at scale. Now, these incumbents are plowing headfirst with ample capital into the EV market, which diminishes Rivian’s ability to take market share. For example:
- Ford (F), which already introduced its Mustang Mach-E and F-150 Lightning, is increasing EV investments to $30 billion through 2025, and recently announced multi-billion dollar battery and EV plants in Tennessee and Kentucky. As recently as May 2021, Ford projects that 40% of its sales, or 2.2 million units based on 2019 (pre-pandemic) sales, will be fully electric by 2030. This level of production would account for 9% of the International Energy Agency’s (IEA) base forecast for EV sales in 2030.
- Volkswagen, Europe’s largest automaker, plans to invest almost $180 billion into EVs through 2025 and projects that 50% of its global sales will be fully electric by 2030, which would equate to 5.5 million vehicles based on 2019 sales. This number of vehicles would account for 21% of IEA’s base forecast for EV sales in 2030.
- General Motors plans to increase its investment into EVs to $35 billion through 2025 and plans to unveil an electric version of its Chevy Silverado in January 2022. General Motors is targeting EV sales of “more than 1 million” by 2025 which would give the company an 8% share of the EV market based on IEA’s base case for 2025.
- Tesla, the current world leader in EV sales, delivered over 800 thousand vehicles through the first three quarters of 2021 and is expected to deliver 1.3 million units in 2022. Despite delays, the company plans to introduce its Cybertruck and is in the process of building additional manufacturing plants.
- Stellantis, parent company of Dodge, Jeep, and Ram, recently announced a partnership with LG to procure battery cells in North America and has noted its goals include having a zero-emission vehicle in every SUV segment by 2025.
Ford, Volkswagen, and General Motors alone are planning to spend at least $245 billion through 2025 and produce nearly 9 million EVs by 2030. These numbers don’t include what other incumbents (Volvo, Honda, Jaguar Land Rover, Porsche, Mercedes, BMW, and more), and other new entrants (NIO, Lucid Motors, Lordstown Motors, and more) will contribute.
Given that Rivian has not delivered a single vehicle to date, it is clearly chasing the competition at this point, and the competition has billions of dollars to spend to win the race.
Incumbents Have Big Plans for SUVs and Trucks
The incumbent manufacturers aren’t just throwing money at general EV goals or targets either. In fact, they’ve laid out clear plans to provide some of the most popular internal combustion vehicles in an EV format. Below are just some of the expected vehicles coming to the SUV/truck EV market:
- GM Hummer – 2021
- Bollinger B2 – 2021/2022
- Ford Lightning – 2022
- Chevy Silverado EV – 2023
- GMC Sierra EV – 2023
- Tesla Cybertruck – 2022/2023
- Canoo Pickup – 2023
- Ram 1500 Electric – 2024
And Vans are Increasingly Competitive Too
Competition will be fierce in the EV delivery van market as well, as manufacturers providing last mile delivery trucks and vans look to maintain existing business with new EV platforms. Below are just some of the many delivery vans in production or scheduled for production.
- Fiat e-Ducato – already on sale in Europe
- Nissan E NV200 – already on sale in Europe
- Ford E Transit – 2022
- BrightDrop EV600 – new GM brand for EV vans – 2022
- Workhorse C1000 – 2022
- Mercedes E Sprinter -already on sale in Europe – late 2023/early 2024 to US
Partnerships Look Overhyped
Many investors may get excited about Rivian’s partnerships with well-known companies like Amazon (AMZN) and Ford. However, when we dig into the details of these partnerships, they’re filled with hype and not much else.
Amazon: In 2019 Rivian announced a partnership with Amazon Logistics Inc., (referred to in the S-1 as “Logistics”) a subsidiary of Amazon which is responsible for last mile delivery of Amazon’s retail operations. While it is reported that Amazon has ordered 100 thousand electric delivery vehicles (EDVs) from Rivian, under the terms of the agreement Amazon is under no obligation to actually purchase any vehicles. From the S-1:
“While the EDV Agreement provides that we will be reimbursed for certain development costs, it does not include any minimum purchase requirements or otherwise restrict Logistics from developing vehicles or collaborating with, or purchasing similar vehicles from, third parties.”
Additionally, Amazon Logistics has exclusive rights to purchase EDVs from Rivian for four years after the date of first vehicle delivery and a right of first refusal for an additional two years.
In other words, Rivian cannot sell EDVs to any other company for four years after delivering its first vehicle to Amazon, whether or not Amazon decides to purchase any EDVs at all. The exclusivity clause of this agreement may significantly hamper Rivian’s ability to capture market share and allow more competitors to enter the EDV market uncontested.
Ford: Rivian also made headlines due to the investments from Ford, which now total nearly $800 million in Class B and D preferred stock. In 2019, Rivian entered into a purchase agreement with a Ford subsidiary, Troy Design and Manufacturing Co (referred to as TDM), for the supply of prototype and pre-production vehicles. Now that Rivian’s factory is up and running, it expects to discontinue purchases for this service from TDM.
However, Rivian is still required to purchase certain key components for its R1 vehicle program exclusively from TDM for the life of the R1 vehicle program. Details on the rest of the partnership are unclear. Ford already cancelled plans to build a Lincoln EV based on Rivian’s platform in 2020, stating that “it would be better to focus our development efforts on Lincoln’s own fully electric vehicle.” More recently, Ford executives left Rivian’s board of directors and Ford noted in a statement that “Rivian is a strategic investment and we're still exploring ways for potential collaboration with them. We don't have anything to announce today.”
While these partnerships were touted as legitimizing Rivian’s business, in reality they look more like arms-length equity investments by Amazon and Ford. In its latest 10-Q, Amazon reported a 20% ownership interest in Rivian. In many respects, these partnerships hinder Rivian’s growth and cost model more than they help the company.
Limited Addressable Market: Unable to Sell Cars in 28 States
As of September 30, 2021, Rivian is only allowed to sell its cars in 22 states and the District of Columbia, or less than half of the United States. In the other 28 states, which include the likes of New York, Texas, and New Jersey, Rivian is restricted from obtaining a dealer license to sell within the state. While Rivian has shown that it can convince states, like Colorado, to allow them to apply for a dealer’s license, it will be a long and expensive process to lobby each state individually.
And Getting Service Could be Troublesome
When it comes to fixing/repairing traditional vehicles, there are any number of options, from DIY, dealers, or auto shops. However, EVs require different repairs and getting service for a Rivian vehicle looks increasingly difficult.
Eight states outright prohibit Rivian from owning or operating a service center providing warranty service. While Rivian does have a plan to address these eight states, the solution is certainly not ideal for customers. Rivian has mobile service units which can be sent from neighboring states to reach customers in prohibited areas, and the company will offer towing services for broken cars to a state with a service location.
However, as of today, Rivian has only six service centers in four states and only 11 mobile service vehicles. For reference, Tesla has nearly 600 store and service locations and a mobile service fleet of nearly 1,100. GM, Ford, and Stellantis have a combined 9,600 dealerships throughout the United States.
Rivian will need to spend significant capital, i.e. burn more cash, to build out a meaningful service network, or else it could see its service centers overfilled with a backlog of repairs, as we’ve already seen with Tesla, which could damage demand.
Stupid Money Risk Looks Low
Given the multi-billion-dollar investments planned by the incumbents, we believe It is highly unlikely that Rivian will be acquired at its lofty expected valuation. Without delivering more than 200 vehicles, Rivian, at the midpoint of its IPO price range, already has a higher market cap than Honda and Nissan, and nearing Stellantis and BMW.
Given that each of the competitors have their own manufacturing plants and existing vehicle platforms to leverage and build EVs, an acquisition of Rivian would be an extremely poor use of capital. Any acquirer would essentially be paying a massive premium to purchase the Rivian brand, which is still unproven in the auto market. It would be more cost effective for potential acquirers to compete with Rivian instead of acquiring them.
Other Red Flags for Investors
With a lofty valuation that implies likely unrealistic improvement in both revenue, profits, and market share, investors should be aware that Rivian’s S-1 also includes these other red flags.
Insiders Have Majority Control: Rivian will have multiple classes of common stock, with class A shares sold to the public and class B shares reserved for the founder and affiliates. Rivian discloses in its S-1 that Class A shares will have one vote per share and Class B shares will have 10 votes per share. After the completion of the IPO, the founder and early investors will hold 69% of the voting rights in the company. Amazon alone will hold 17% of the voting power.
In other words, despite new investors paying a premium to buy the IPO and provide capital to the company, Rivian’s insiders and other owners will continue to control the company, and new shareholders will have little to no control over corporate governance.
No Non-GAAP Metrics, Yet: Many unprofitable companies present non-GAAP metrics to appear more profitable than they really are. However, Rivian discloses no non-GAAP metrics in its entire S-1. However, investors need to be aware that should such disclosure practice change, there is always a risk that non-GAAP metrics could be used to manipulate earnings going forward.
We Don’t Know If We Can Trust the Financials: Investors should take Rivian’s reported numbers with a grain of salt because the company identified a material weakness in its internal control over financial reporting. Specifically, the company identified a deficiency related to “controls to address segregation of duties across financially relevant functions and information technology general controls over tools and applications used in financial reporting.” As an emerging growth company, Rivian is not required to have an independent auditor provide an opinion on internal controls, so we’re glad the company chose to disclose this information.
However, the company makes no assurances that the issues have been fixed, nor that it has identified all existing material weaknesses. From the S-1:
“We will not be able to fully remediate these material weaknesses until these steps have been completed and have been operating effectively for a sufficient period of time…accordingly, we cannot assure you that we have identified all, or that we will not in the future have additional, material weaknesses.”
Weaknesses in internal controls increase the risk that the company’s financials are fraudulent and/or misleading.
Emerging Growth Status Limits Transparency: By electing to operate as an “Emerging Growth Company”, Rivian is exempt from certain requirements that are beneficial to shareholders. For instance, and as noted above the SEC does not currently require Rivian to have an independent auditor provide an opinion on internal controls. Additionally, Rivian is not required to provide information on executive compensation structure and can delay adoption of certain accounting procedures, which limit the transparency of its financial statements. Get more details on the risks of investing in emerging growth companies here.
Critical Details Found in Financial Filings By Our Robo-Analyst Technology
Fact: we provide superior fundamental data and earnings models – unrivaled in the world.
Proof: Core Earnings: New Data and Evidence, published in The Journal of Financial Economics.
Below are specifics on the adjustments we make based on Robo-Analyst findings in Rivian’s S-1:
Income Statement: we made $57 million in adjustments, with a net effect of removing $35 million in non-operating expenses. You can see all the adjustments made to Rivian’s income statement here.
Balance Sheet: we made $781 million in adjustments to calculate invested capital, with a net effect of decreasing invested capital by $725 million. The most notable adjustment was $3 million in operating leases. This adjustment represented <1% of reported net assets. You can see all the adjustments made to Rivian’s balance sheet here.
Valuation: we made $5.4 billion in adjustments to shareholder value, all of which decreased shareholder value. The largest adjustment to shareholder value was $5.2 billion in preferred capital. This adjustment represents 10% of the midpoint of Rivian’s IPO valuation. You can see all the adjustments made to Rivian’s valuation here.
This article originally published on November 3, 2021.
Disclosure: David Trainer, Kyle Guske II, Alex Sword, and Matt Shuler receive no compensation to write about any specific stock, style, or theme.
Follow us on Twitter, Facebook, LinkedIn, and StockTwits for real-time alerts on all our research.
[1] Only Core Earnings enable investors to overcome the inaccuracies, omissions and biases in legacy fundamental data and research, as proven in Core Earnings: New Data & Evidence, written by professors at Harvard Business School (HBS) & MIT Sloan and published in The Journal of Financial Economics.